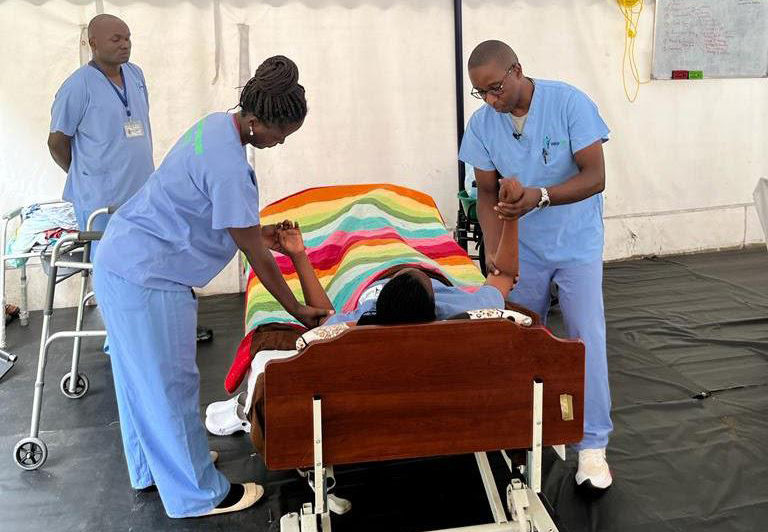
Our Homecare and Geriatrics Training targets professionals who provide care to elderly individuals and persons with unfavorable health conditions, either in their homes or in other settings like in-patient health facilities. This training typically covers a range of topics to ensure that caregivers are well-prepared to meet the physical, emotional and medical needs of older adults and persons with unfavorable health conditions.